Blog
- Home
- Blog
Bridge Crane Selection Guide: How to Pick the Best Crane for Your Workshop
A bridge crane, also known as an overhead crane, is a fixed lifting machine designed for short-distance handling of medium and small loads. It consists of a movable bridge that spans the gap between two parallel runways, allowing precise lifting and transportation of materials across a defined area.
Bridge cranes are widely used in workshops, factories, assembly lines, warehouses, and maintenance facilities, where efficient and safe material handling is essential. These cranes play a vital role in improving workflow efficiency and ensuring operational safety during the lifting and movement of heavy loads.
Proper bridge crane selection is crucial for optimizing productivity, ensuring workplace safety, and controlling operational costs. Choosing the right type and configuration can significantly reduce downtime, improve workflow, and minimize potential risks during operation.
Ⅰ. Basic Structure of a Bridge Crane
The main structure of a bridge crane consists of one or two main girders mounted on parallel runways along both sides of a workshop or building. A hoist runs along the girder, while a trolley on each side enables coordinated three-dimensional movement.
The lifting mechanism handles the vertical movement of loads (lifting and lowering), the trolley mechanism provides lateral motion (left and right), and the bridge traveling mechanism enables longitudinal motion (forward and backward).
Together, these components allow for precise positioning and smooth material handling across the entire working area.
Ⅱ. Working Principle of a Bridge Crane
A bridge crane operates through the coordinated movement of three main mechanisms: the bridge traveling mechanism (long travel), the trolley traveling mechanism (cross travel), and the hoisting mechanism (lifting). These systems work together on dedicated runways and rails to achieve accurate vertical, transverse, and longitudinal material handling.
The main working motions include:
•Bridge Traveling (Long Travel):
The bridge moves forward and backward along the runways on both sides of the workshop, allowing long-distance transportation of heavy loads.
•Trolley Traveling (Cross Travel):
The trolley moves side to side along the girder, providing flexible load positioning within the crane’s coverage area.
•Hoisting (Lifting Motion):
The hook or lifting device moves up and down via a wire rope or chain system, enabling safe and efficient lifting, lowering, and unloading of materials.
Understanding the structure and working principle is the first step in bridge crane selection, as it helps determine the type and configuration best suited for your workshop layout and operational needs.
Through the coordinated movement of these mechanisms, the bridge crane efficiently performs material lifting, transportation, and unloading operations.
This high-efficiency system is widely used in workshops, warehouses, and various industrial environments, where precise and reliable material handling is essential.
Ⅲ. Common Types of Bridge Cranes
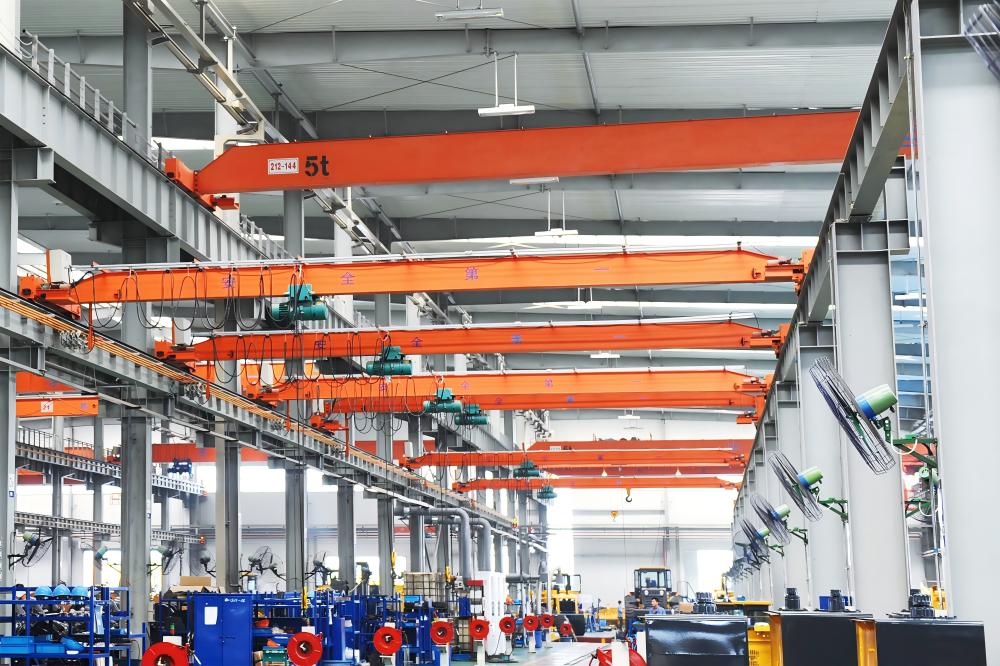
1. Single Girder Bridge Crane (Model LD)
The Single Girder Bridge Crane (LD type) is one of the most commonly used and widely applied models among light-duty bridge cranes. Featuring a compact design and high structural rigidity, it provides a cost-effective solution for efficient material handling.
This crane is typically equipped with CD, MD, or HC type electric hoists, suitable for light to medium lifting tasks.
Its rated load capacity ranges from 1 ton to 20 tons, meeting various industrial lifting needs.
- Application Scenarios:
The single girder bridge crane is ideal for small manufacturing workshops, assembly lines, warehouses, and maintenance facilities.
It is especially suited for light industrial environments that require frequent handling of small and medium loads, such as electronic assembly, mechanical processing, or component handling.
2. Low Headroom Bridge Crane
The Low Headroom Bridge Crane is specifically designed for facilities with limited vertical space.
With its optimized structural design, the hook can reach a position closer to the bottom of the main girder when lifted to the highest point.
This innovative configuration effectively reduces the required clearance height while maximizing the available lifting height, making it an ideal solution for workshops or work areas with restricted overhead space.
- Application Scenarios:
The low headroom bridge crane is suitable for old factories, warehouses, or low-rise buildings where ceiling height is limited.
It is especially popular in industries such as food processing, textile production, and small logistics centers, where vertical space utilization is critical to maintaining productivity.
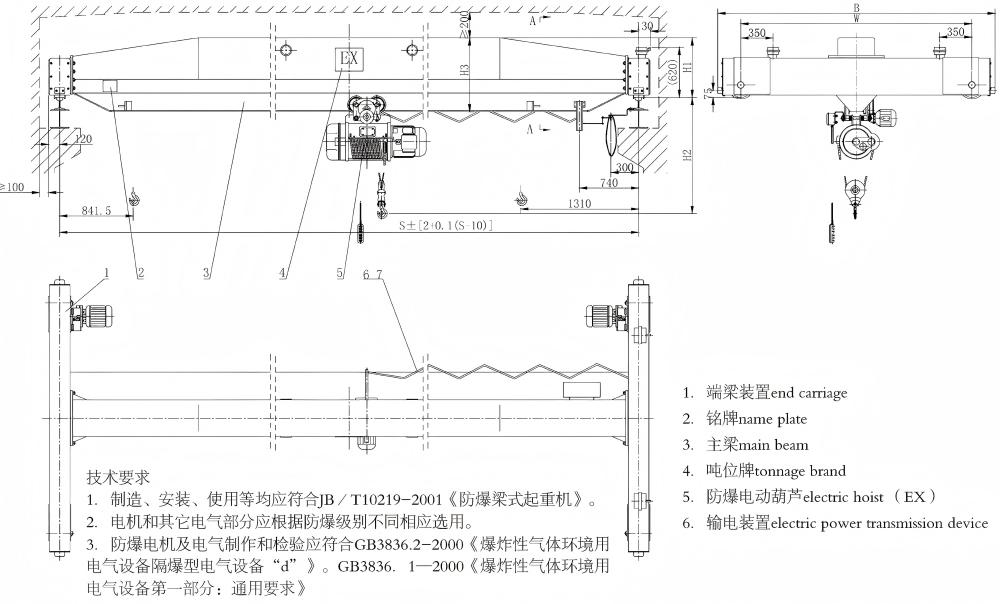
3. Explosion-Proof Bridge Crane (LB, QB)
The Explosion-Proof Bridge Crane (models LB and QB) is designed based on the standard bridge crane structure, with enhanced safety features to ensure reliable operation in hazardous or explosive environments.
It incorporates explosion-proof motors and optimized electrical components, along with mechanical safety protection systems, effectively preventing the risk of fire or explosion.
The explosion protection rating is identified by the special marking “Ex”, indicating compliance with safety standards for explosive atmospheres.
- Application Scenarios:
The explosion-proof bridge crane is engineered for high-risk industrial environments, including chemical plants, oil and gas facilities, coal mines, paint workshops, and pharmaceutical factories.
It provides safe, efficient, and stable material handling in areas where flammable gases, vapors, or dust may be present.
4. Double Girder Bridge Crane (QD)
The Double Girder Bridge Crane (QD type) features two parallel main girders as its core structural element, providing exceptional load-bearing capacity and operational stability.
This robust design allows the crane to handle heavier loads while maintaining structural integrity and durability, significantly extending the service life of the equipment.
- Application Scenarios:
The double girder bridge crane is ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications, such as steel plants, shipyards, large machinery manufacturing workshops, and port terminals.
It is specifically designed for lifting and transporting oversized or ultra-heavy materials, including steel components, large machinery, and heavy molds.
5. Double Girder Hoist Bridge Crane (LH Type)
The Double Girder Hoist Bridge Crane (LH type) consists of four main components: the electric hoist trolley, bridge frame, long-travel mechanism, and electrical control system.
Its lifting mechanism uses a fixed wire rope electric hoist, supporting both cab control and ground remote control modes.
This configuration ensures flexible, convenient, and reliable operation, while an optional variable frequency drive (VFD) can be added to further enhance performance and lifting precision.
- Application Scenarios:
The LH type bridge crane is designed for medium to heavy-duty lifting operations, making it ideal for automobile manufacturing plants, electrical equipment assembly workshops, steel structure fabrication facilities, and large warehouse centers.
It is particularly suitable for industrial environments that require high lifting accuracy and smooth, flexible operation.
Ⅳ. Comparison Between Single Girder and Double Girder Bridge Cranes
When performing a bridge crane selection, understanding the differences between single girder and double girder bridge cranes is essential.
Each type has distinct advantages in terms of structure, cost, maintenance, and performance, making them suitable for different industrial applications.
| Comparison Item | Single Girder Bridge Crane | Double Girder Bridge Crane |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | One main girder; simpler and lighter design | Two main girders; stronger and more rigid construction |
| Price | Lower initial cost; more economical | Higher cost due to additional materials and components |
| Maintenance | Easier and cheaper; fewer components | More complex, but maintenance intervals are longer |
| Performance | Suitable for light to medium loads up to 20 tons | Handles loads above 20 tons with better stability and higher lifting speed |
Overall, the single girder bridge crane is ideal for mechanical manufacturing, small assembly workshops, and general industrial use.
In contrast, the double girder bridge crane is better suited for steel structure fabrication, heavy machinery production, and environments requiring high lifting capacity and stability.
Ⅴ. Key Points for Bridge Crane Selection and Customization
Selecting and customizing a bridge crane requires careful consideration of several critical factors to ensure efficiency, safety, and reliability in your workshop or industrial facility.
1. Determine Bridge Crane Parameters
•Lifting Capacity: Calculate the maximum load (kg or tons) to be lifted, including a safety margin.
•Lifting Height: Measure the distance from the hook center to the ground and account for workshop height.
•Span: Measure the distance between runway centerlines, constrained by workshop width.
•Duty Class: Choose a duty classification (A1–A8) based on load intensity and operational frequency, suitable for light to extra-heavy tasks.
•Working Environment: Evaluate temperature, humidity, and presence of hazardous substances (e.g., dust, flammable gases) to select the appropriate crane type, such as explosion-proof models.
2. Select the Hoisting Mechanism
•Choose between a wire rope electric hoist or chain hoist according to load requirements.
•Determine the lifting speed and acceleration/deceleration parameters to meet operational efficiency.
•Ensure safety features such as limit switches, emergency stop, and overload protection are included.
3. Choose the Control System
•Select manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic control based on operational needs.
•Ensure a user-friendly interface, integrated safety functions, and compatibility with other equipment.
4. Consider Electrical and Power Requirements
•Determine the power supply (voltage, frequency) and transmission method (e.g., cable reel or busbar).
•Calculate the load requirements and configure motors, controllers, and electrical components to guarantee stable operation.
5. Pay Attention to Safety Features
•Include limit switches to prevent over-travel and overload protection to avoid accidents.
•Conduct regular inspections, focusing on wiring, brakes, and structural integrity. Key maintenance includes lubrication and timely replacement of worn parts.
•Reliable after-sales support ensures fast access to spare parts and service, minimizing downtime.
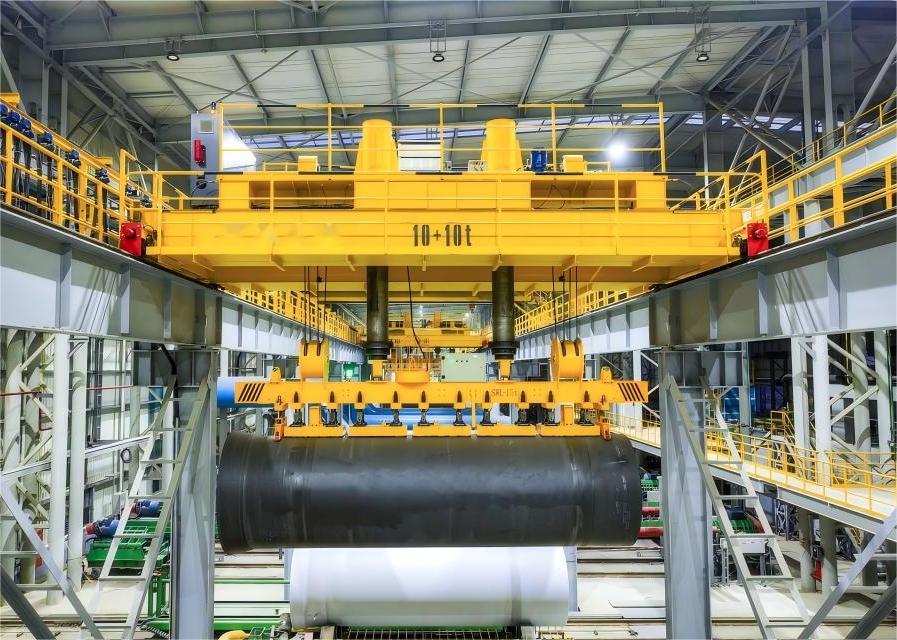
This diagram illustrates the key components and layout of a customized explosion-proof bridge crane, including the main girders, hoist trolley, bridge traveling mechanism, and safety protection systems.
Such customized designs ensure safe and reliable operation in hazardous environments, allowing efficient material handling while meeting specific industrial requirements.
Ⅵ. Steps to Customize a Bridge Crane
Creating a customized bridge crane tailored to your workshop requirements is a straightforward process. Follow these key steps:
1. Contact Us
Reach out to discuss your bridge crane needs and operational requirements.
2. Provide Specifications
Clearly provide the following information:
•Type of load to be lifted
•Lifting capacity (tons)
•Lifting height (meters)
•Span (meters)
•Travel speed (meters/min)
•Travel distance (meters)
•Power supply voltage
•Control method (manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic)
•Duty classification
Once your custom crane is designed and manufactured, prepare to welcome a new stage of efficient production in your workshop!
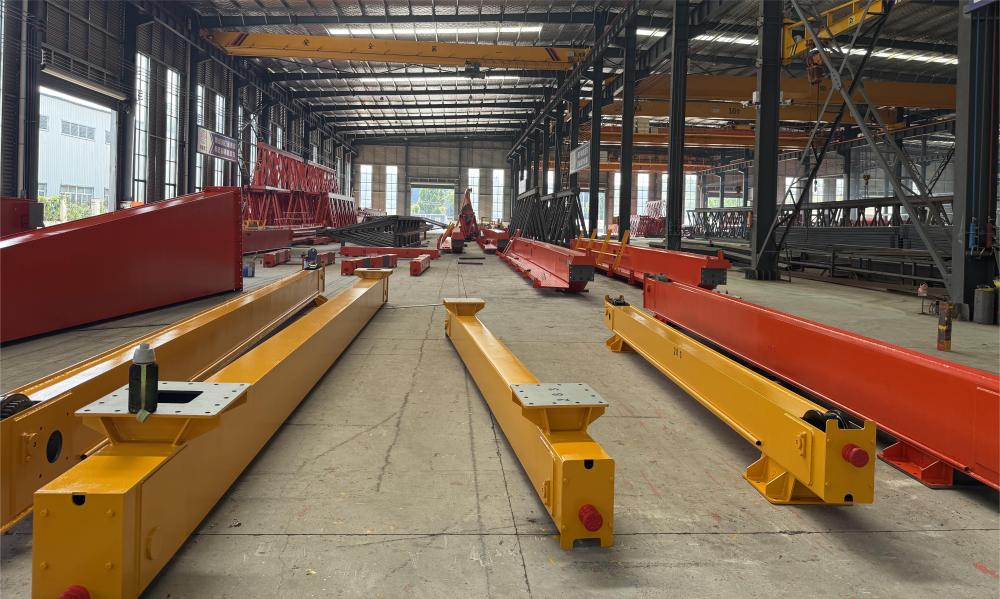

The bridge crane ordered by our client is now ready for packaging and dispatch. This marks the final stage before delivery, ensuring the equipment reaches the customer safely and on schedule.
Ⅶ .Why Choose HSCRANE Bridge Cranes
1. High-Standard Design (FEM/DIN)
Our bridge cranes strictly adhere to FEM (European Crane Design Standards) and DIN (German Industrial Standards), ensuring structural strength, operational stability, and durability at international leading levels. From light-duty (A1-A3) to extra heavy-duty (A8), each crane undergoes precise design and rigorous testing to guarantee long-term, high-efficiency performance.
2. Comprehensive Customization Solutions
HSCRANE offers tailored solutions to meet the unique needs of various workshops:
•Span: Precisely designed to match workshop width, suitable for small to large-scale factories.
•Lifting Height: Optimized hook design, ideal for low-clearance environments.
•Operation Modes: Options include manual, remote control, cabin operation, or variable frequency control.
•Special Environments: Features for high-temperature, dusty, or explosive environments, including heat-resistant, explosion-proof, or corrosion-resistant configurations. We provide 3D design drawings and simulated operation plans to ensure the equipment perfectly aligns with your requirements.
3. Global Export and Service Network
HSCRANE products are exported to Asia, Europe, Africa, and the Americas, with expertise in international standards and logistics. We offer global technical support, spare parts supply, and maintenance services to ensure fast delivery and reliable operation, minimizing downtime.
Customer Case Study:
In a manufacturing plant in Southeast Asia, HSCRANE delivered a customized 10+10 ton double girder bridge crane (QD type), boosting mold handling efficiency by 30%. This tailored solution optimized the workshop’s workflow, demonstrating the value of precise bridge crane selection for enhanced productivity.
Selecting the appropriate bridge crane is crucial for boosting productivity, ensuring safety, and reducing costs. Key criteria for bridge crane selection include:
- Load Capacity: Determine the maximum weight the crane needs to lift.
- Lifting Height: Ensure the crane meets the required vertical lifting distance.
- Duty Cycle: Match the crane’s work class (e.g., A1-A8) to your operational intensity.
- Special Environmental Needs: Consider high-temperature, dusty, or explosive environments for specialized features like heat-resistant or explosion-proof configurations.
Partnering with a professional supplier like HSCRANE minimizes trial-and-error costs and ensures a tailored solution for your bridge crane for workshop needs.
Take Action Now:
Contact HSCRANE today for a customized bridge crane solution! Visit our website or call our global service hotline to access free consultations and expert support. Start your journey to efficient production now!
Recent Post